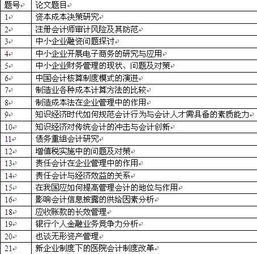
1.我想知道博弈论的
General equilibrium theory can be viewed as a specialized branch of game theory that deals with trade and production,and typically with a relatively large number of individual consumers and producers.It is widely used in the macroeconomic analysis of broad based economic policies such as monetary or tax policy,in finance to analyze stock markets,to study interest and exchange rates and other prices.In recent years,political economy has emerged as a combination of general equilibrium theory and game theory in which the private sector of the economy is modeled by general equilibrium theory,while voting behavior and the incentive of governments is analyzed using game theory.Issues studied include tax policy,trade policy,and the role of international trade agreements such as the European Union.。
2.博弈论的论文
博弈论(Game Theory),又称为对策论,或者赛局理论,应用数学的一个分支,是使用严谨的数学模型研究冲突对抗条件下最优决策问题的理论。目前在生物学,经济学,国际关系,计算机科学,政治学,军事战略和其他很多学科都有广泛的应用。博弈论也应用于数学的其他分支,如概率,统计和线性规划,生物学家使用博弈理论来理解和预测进化(论)的某些结果。博弈论主要研究公式化了的激励结构(游戏或者博弈)间的相互作用,是研究具有斗争或竞争性质现象的数学理论和方法,也是运筹学的一个重要学科。博弈论作为一门正式学科,博弈论是在20世纪40年代形成并发展起来的。
博弈论考虑游戏中的个体的预测行为和实际行为,并研究它们的优化策略。表面上不同的相互作用可能表现出相似的激励结构(incentive structure),所以他们是同一个游戏的特例。其中一个有名有趣的应用例子是囚徒困境悖论(Prisoner's dilemma)。具有竞争或对抗性质的行为成为博弈行为。在这类行为中,参加斗争或竞争的各方各自具有不同的目标或利益。为了达到各自的目标和利益,各方必须考虑对手的各种可能的行动方案,并力图选取对自己最为有利或最为合理的方案。比如日常生活中的下棋,打牌等。博弈论就是研究博弈行为中斗争各方是否存在着最合理的行为方案,以及如何找到这个合理的行为方案的数学理论和方法。
博弈论根据其所采用的假设不同而分为合作博弈理论和非合作博弈理论。前者主要强调的是团体理性;而后者主要研究人们在利益相互影响的局势中如何选择策略使得自己的收益最大,即策略选择问题,强调的是个人理性。目前经济学家谈到博弈论主要指的是非合作博弈,也就是各方在给定的约束条件下如何追求各自利益最大化,最后达到力量均衡。在这一点上,博弈论和经济学家的研究模式是完全一样的。经济学越来越转向人与人关系的研究,特别是人与人之间行为的相互影响和相互作用,人与人之间利益和冲突、竞争与合作,而这正是博弈论的研究对象。此外,博弈论以不同的所持信息又可以分为完美博弈、完全博弈和不完全博弈(贝叶斯博弈);以博弈进行的次数或者持续长短可以分为有限博弈和无限博弈;以表现形式也可以分为一般型(战略型)或者展开型,等等。
博弈论在国际贸易中的运用如:任何一个国家在国际贸易中都面临着保持贸易自由与实行贸易保护主义的两难选择。贸易自由与壁垒问题,也是一个“纳什均衡”,这个均衡是贸易双方采取不合作博弈的策略,结果使双方因贸易战受到损害。X国试图对Y国进行进口贸易限制,比如提高关税,则Y国必然会进行反击,也提高关税,结果谁也没有捞到好处。反之,如X和Y能达成合作性均衡,即从互惠互利的原则出发,双方都减少关税限制,结果大家都从贸易自由中获得了最大利益,而且全球贸易的总收益也增加了。
当代博弈论的主要理论家有:约翰·福布斯·纳什(John Forbes Nash Jr)、约翰·C·海萨尼、莱因哈德·泽尔腾,他们3人因对博弈论的突出贡献而同时获得1994年的瑞典银行经济学奖);罗伯特·奥曼(Robert J. Aumann)、美国人托马斯·谢林(Thomas C. Schelling)他们2人获得2005年诺贝尔经济学奖;以及肯·宾摩尔、戴维·克瑞普斯,阿里尔·鲁宾斯坦等。
3. John Nash 和博弈论的英文版资料
给你找了一些,希望对你有帮助:Nash, John Forbes(born June 13, 1928, Bluefield, W.Va., U.S.) U.S. mathematician. He earned a doctorate from Princeton University at 22. He began teaching at Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1951 but left in the late 1950s because of mental illness; thereafter he was informally associated with Princeton. Beginning in the 1950s with his influential thesis “Non-cooperative Games,” Nash established the mathematical principles of game theory. His theory, known as the Nash solution or Nash equilibrium, attempted to explain the dynamics of threat and action among competitors. Despite its practical limitations, it was widely applied by business strategists. He shared the 1994 Nobel Prize in Economics with John C. Harsanyi (b. 1920) and Reinhard Selten (b. 1930). A film version of his life, A Beautiful Mind (2001), won an Academy Award for best picture.game theoryn.A mathematical method of decision-making in which a competitive situation is analyzed to determine the optimal course of action for an interested party, often used in political, economic, and military planning. Also called theory of games.games, theory of, group of mathematical theories first developed by John Von Neumann and Oskar Morgenstern. A game consists of a set of rules governing a competitive situation in which from two to n individuals or groups of individuals choose strategies designed to maximize their own winnings or to minimize their opponent's winnings; the rules specify the possible actions for each player, the amount of information received by each as play progresses, and the amounts won or lost in various situations. Von Neumann and Morgenstern restricted their attention to zero-sum games, that is, to games in which no player can gain except at another's expense.This restriction was overcome by the work of John F. Nash during the early 1950s. Nash mathematically clarified the distinction between cooperative and noncooperative games. In noncooperative games, unlike cooperative ones, no outside authority assures that players stick to the same predetermined rules, and binding agreements are not feasible. Further, he recognized that in noncooperative games there exist sets of optimal strategies (so-called Nash equilibria) used by the players in a game such that no player can benefit by unilaterally changing his or her strategy if the strategies of the other players remain unchanged. Because noncooperative games are common in the real world, the discovery revolutionized game theory. Nash also recognized that such an equilibrium solution would also be optimal in cooperative games. He suggested approaching the study of cooperative games via their reduction to noncooperative form and proposed a methodology, called the Nash program, for doing so. Nash also introduced the concept of bargaining, in which two or more players collude to produce a situation where failure to collude would make each of them worse off.The theory of games applies statistical logic to the choice of strategies. It is applicable to many fields, including military problems and economics. The Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences was awarded to Nash, John Harsanyi, and Reinhard Selten (1994) and to Robert J. Aumann and Thomas C. Schelling (2005) for work in applying game theory to aspects of economics./topic/john-forbes-nash。
4.英语翻译“对于博弈论中非常简单的一个模型——囚徒的困境,对于它
百度翻译呗! "For a prisoner -- game theory model is very simple dilemma, for its resolution is rich and colorful, from this small example we can derive some famous theory in economics, which will be used in the field of economics deep in game theory, which is a characteristic this subject, methods for small problems. The prisoner's dilemma is a basic fundamental."。
5.博弈论的论文
博弈论(Game Theory),又称为对策论,或者赛局理论,应用数学的一个分支,是使用严谨的数学模型研究冲突对抗条件下最优决策问题的理论。目前在生物学,经济学,国际关系,计算机科学,政治学,军事战略和其他很多学科都有广泛的应用。博弈论也应用于数学的其他分支,如概率,统计和线性规划,生物学家使用博弈理论来理解和预测进化(论)的某些结果。博弈论主要研究公式化了的激励结构(游戏或者博弈)间的相互作用,是研究具有斗争或竞争性质现象的数学理论和方法,也是运筹学的一个重要学科。博弈论作为一门正式学科,博弈论是在20世纪40年代形成并发展起来的。
博弈论考虑游戏中的个体的预测行为和实际行为,并研究它们的优化策略。表面上不同的相互作用可能表现出相似的激励结构(incentive structure),所以他们是同一个游戏的特例。其中一个有名有趣的应用例子是囚徒困境悖论(Prisoner's dilemma)。具有竞争或对抗性质的行为成为博弈行为。在这类行为中,参加斗争或竞争的各方各自具有不同的目标或利益。为了达到各自的目标和利益,各方必须考虑对手的各种可能的行动方案,并力图选取对自己最为有利或最为合理的方案。比如日常生活中的下棋,打牌等。博弈论就是研究博弈行为中斗争各方是否存在着最合理的行为方案,以及如何找到这个合理的行为方案的数学理论和方法。
博弈论根据其所采用的假设不同而分为合作博弈理论和非合作博弈理论。前者主要强调的是团体理性;而后者主要研究人们在利益相互影响的局势中如何选择策略使得自己的收益最大,即策略选择问题,强调的是个人理性。目前经济学家谈到博弈论主要指的是非合作博弈,也就是各方在给定的约束条件下如何追求各自利益最大化,最后达到力量均衡。在这一点上,博弈论和经济学家的研究模式是完全一样的。经济学越来越转向人与人关系的研究,特别是人与人之间行为的相互影响和相互作用,人与人之间利益和冲突、竞争与合作,而这正是博弈论的研究对象。此外,博弈论以不同的所持信息又可以分为完美博弈、完全博弈和不完全博弈(贝叶斯博弈);以博弈进行的次数或者持续长短可以分为有限博弈和无限博弈;以表现形式也可以分为一般型(战略型)或者展开型,等等。
博弈论在国际贸易中的运用如:任何一个国家在国际贸易中都面临着保持贸易自由与实行贸易保护主义的两难选择。贸易自由与壁垒问题,也是一个“纳什均衡”,这个均衡是贸易双方采取不合作博弈的策略,结果使双方因贸易战受到损害。X国试图对Y国进行进口贸易限制,比如提高关税,则Y国必然会进行反击,也提高关税,结果谁也没有捞到好处。反之,如X和Y能达成合作性均衡,即从互惠互利的原则出发,双方都减少关税限制,结果大家都从贸易自由中获得了最大利益,而且全球贸易的总收益也增加了。
当代博弈论的主要理论家有:约翰·福布斯·纳什(John Forbes Nash Jr)、约翰·C·海萨尼、莱因哈德·泽尔腾,他们3人因对博弈论的突出贡献而同时获得1994年的瑞典银行经济学奖);罗伯特·奥曼(Robert J. Aumann)、美国人托马斯·谢林(Thomas C. Schelling)他们2人获得2005年诺贝尔经济学奖;以及肯·宾摩尔、戴维·克瑞普斯,阿里尔·鲁宾斯坦等。
6.有关博弈论的英文书籍
第一本、Agreeing to Cooperate: Cooperative Game Theory and Solution Concepts CONTENTS 1. Cooperative Game Theory 2. Coalitional Games with Transferable Payoffs 3. Payoff Profiles and the Core 4. Example: Treasure Hunting 5. Application: Intra-Firm Bargaining 6. The Core of the Firm 7. A Production Example 8. Marginal Contributions and the Shapley Value 9. Expected Marginal Contributions 10. Application: The Shapley Value and a Worker 11. The Shapley Value for a Worker: The Easy Way 12. Application: The Shapley Value and the Firm 13. The Shapley Value for a Firm: The Easy Way 14. Justifying the Shapley Value 15. Behaviour and Scope of the Firm 16. The Over-Hiring of Labour 17. Investment Incentives and Frontload Factors 18. Economies of Scope and the Effect of Synergies 第二本、Springer07《合作博弈导论》(Introduction to the Theory of Cooperative Games 2nd ed) Introduction to the Theory of Cooperative Games (Theory and Decision Library C) (Hardcover) by Bezalel Peleg (Author), Peter Sudhölter (Author) Hardcover: 328 pages Publisher: Springer; 2nd ed. edition (October 3, 2007) Language: English Book Description This book systematically presents the main solutions of cooperative games: the core, bargaining set, kernel, nucleolus, and the Shapley value of TU games, and the core, the Shapley value, and the ordinal bargaining set of NTU games. To each solution the authors devote a separate chapter wherein they study its properties in full detail. Moreover, important variants are defined or even intensively analyzed. The authors also investigate in separate chapters continuity, dynamics, and geometric properties of solutions of TU games. The study culminates in uniform and coherent axiomatizations of all the foregoing solutions (excluding the bargaining set). Such axiomatizations have not appeared in any book. Moreover, the book contains a detailed analysis of the main results on cooperative games without side payments. Such analysis is very limited or non-existent in other books on game theory. 第三本、Models in Cooperative Game Theory (Springer 2008) Springer 2008 Models in Cooperative Game Theory (Hardcover) by Rodica Branzei (Author), Dinko Dimitrov (Author), Stef Tijs (Author) Publisher: Springer; 2nd ed. edition (April 1, 2008) Language: English 第四本、《动态合作――尖端博弈论》 作者: 杨荣基 副标题: 尖端博弈论--较诺奖贡献更复杂的解法与数式 ISBN: 9787509201275 页数: 269 出版社: 中国市场出版社 定价: 40.0 装帧: 平装 出版年: 2007-2-1 两位在世界上处领导地位的专家及博弈论先驱—杨荣基教授及彼得罗相教授-合著的《随机微分合作博弈》一书,将会首次为『随机合作』提供基础及实体的解法。
在这个极其艰深的课题中,两位作者用他们的研究理念创出崭新及精确的处理方法。此书将成为这方面研究的划时代经典著作。
----数学大师,美国加州伯克利大学利智文教授(George Leitman) 这本由一位世界最出色的动态博弈论家与一位世界顶尖的“随机微分合作对策”学家合作的巨著,将成为经典之作。他们为精确计算“得偿分配程序”所创的数学定理,是“随机微分合作对策”理论的一项突破。
此书在“动态平稳”研究的发展--特别是“子博弈一致”--实在是李亚普诺夫、蓬特里亚金及祖博夫等在这方面的杰出传统的延续。 --俄罗斯科学院应用数学研究院院长马扎洛夫教授(Vladimir Mazalov) “较诺奖贡献更复杂的解法和数式” 摘要: 尖端博弈论--较诺奖贡献更复杂的解法与数式 / 杨荣基 / 中国市场出版社 简介 · · · · · · 博弈不但串联起人生的每个环节,也串联起整个人类和世界。
博弈论的发展已经令经济学起了翻天覆地的变化,时至今日它已经成为经济分析的标准工具。 在博弈论的研究和应用范畴中,动态微分博弈论是最艰深而成果极大的分支,它研究的是随时间而转变的决策互动,动态博弈的困难在于,在前一刻最优的决策在下一刻可能不再为最优,因此在求解上发生很大的困难。
合作是经济研究中的另一个重要主题,成功的合作往往能通过协同效应,发挥各方的所长与优势,共同创造共赢的局面,甚至实现帕累托最优。但是,由于参与博弈的各方利益间存在着冲突,搭便车的问题可能导致合作受到破坏。
而动态的环境下,合作将变得尤其困难。然而现实的环境充满动态合作情况,世界贸易谈判、境内境外投资、跨国污染控制、地方合作等等都是这样的例子。
此外,由于在时间的的流动中还包含着随机发展的变化,令动态博弈的的复杂性大为增加,这种复杂的决策情况称国随机动态微分合作。在这些情况下,合作问题求解所涉及的数学理论和技术较诺奖贡献更为复杂。
可以说,如何解决随机动态环境下的合作问题是博弈论应用和发展的一个重大课题。 本书作者杨荣基和皮得罗相教授是世界知名的博弈论学者,他们。


 0
0 2023-12-07 08:51
2023-12-07 08:51